NeuroShell Run-Time Server
The NeuroShell Run-Time Server allows you to fire neural networks created with the NeuroShell
Predictor or NeuroShell Classifier from either a simple interface, from your own computer
programs, from Excel spreadsheets or from a web page (Windows based servers only). That means you can use the neural network models with new
data without using our interface.
The NeuroShell Run-Time Server has several distinct programs:
1. Two different NeuroShell Run-Time ActiveX
controls (NSRUN.OCX and NSRUN.DLL) - Distributable
2. NeuroShell Fire program (NSFIRE.EXE)
3. NeuroShell Fire Excel Add-in (NSFIRE.XLA)
4. NeuroShell Run Excel Add-in (NSRUN.XLA) - Distributable
5. NeuroShell Run Wrapper DLL (NSWRAP.DLL) - Distributable
1. NeuroShell Run-Time ActiveX Controls (NSRUN.OCX
and NSRUN.DLL)
Use the NeuroShell Run-Time ActiveX controls to embed the firing of your neural networks into your own
programs. The Run-Time Server provides two separate ActiveX controls. In your program you simply place a call to a
control's method ‘Predict’, passing the location of your trained neural network and the neural network's
inputs. The call returns the neural network's output, which you may use as needed inside your
program. You may call the method Predict as many times as required for as many neural networks as
needed.
NeuroShell Run-Time ActiveX controls work with programming languages such
as Microsoft® Visual Basic®, C++, and Borland™ Delphi™. Note, however, that it
is much easier to use Microsoft Visual Basic to create applications with
ActiveX controls than it is
to use other languages. You are strongly urged to use Visual Basic to call
ActiveX controls
because it makes it much easier to use them.
The NSRUN.DLL ActiveX control encapsulates a method called PredictFromWeb which works in the Active Server Page (ASP) programming environment. This means you can install the Run-Time Server on a Windows-based Web server and fire your neural networks from the ASP through the Internet. The product contains two types of examples of firing the neural networks on the web: one example is for regular ASP programming; the other is for VB.NET programming.
2. NeuroShell Fire Program
(NSFIRE.EXE)
The NeuroShell Fire program (NSFIRE.EXE) is a stand-alone program that
allows you to interactively enter input values and instantly view the output for one
example at a time. It can also create a log file of your inputs and predictions.

3. NeuroShell Fire Excel Add-in (NSFIRE.XLA)
The NeuroShell Fire Excel Add-In enables you to fire your neural networks from within an
Excel spreadsheet. This program uses the file named NSFIRE.XLA.
There are two ways to fire the neural network from within Excel: the Dialog Box or the FireNet
function.
Dialog Box
A dialog box guides you in placing neural network calls into your spreadsheet.

Next, specify the range which contains the
input values and the column where the output values will be placed. The output of the
neural network is placed in the specified column. (You can select multiple rows of data as the
input range and the neural network will provide answers for all selected rows.)
FireNet Function Call
To use the FireNet Function, you do not need to start the Add-In from the Excel Tools
Menu. Instead you will place a call of the function FireNet in each cell where you want to
get results from the neural network. The function FireNet specifies the range of the input
values. The output will be placed in the cell that contains the FireNet function. This
method recalls the neural network each time the spreadsheet recalculates so the neural network's results
are updated.
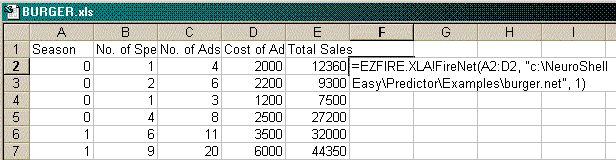
The following example returns the prediction generated by the neural network stored in the file
C:\NEUROSHELL\PREDICTOR\EXAMPLES\BURGER.NET. The neural network's four inputs are located in
cells A2:D2. The predictions are made using Enhanced Generalization.
=EZFIRE.XLA!FireNet(A2:D2, "C:\NeuroShell\Predictor\Examples\BURGER.NET", 1)
4. NeuroShell Run Excel Add-in (NSRUN.XLA)
This program uses the file NSRUN.XLA that allows you to call a neural network trained in either
the NeuroShell Predictor or NeuroShell Classifier from within a cell in an Excel
spreadsheet.
This is a version of the program that may be sent to people who do not own either the
Predictor or Classifier software. The software that you distribute to your users should
include the file NSRUN.XLA, which the user loads as an Excel Add-In.
To use this program the user places a call of the function FireNet in each cell where
he/she wants to get results from the neural network. The function FireNet specifies the range of
the input values. The output will be placed in the cell that contains the FireNet
function. This method recalls the neural network each time the spreadsheet recalculates so the
neural network's results are updated.
5.
NeuroShell Run Wrapper DLL (NSWRAP.DLL)
This is a regular Dynamic Link Library (DLL) to call the run-time functions. The
name of the DLL is NSWRAP.DLL. This DLL was built to facilitate the usage
of the Run-Time from programming languages such as C/C++ and Pascal.
NSWRAP.DLL represents itself as a wrapper around the
NeuroShell Run-Time OLE Automation server NSRUN.DLL. In other words, the
NSWRAP.DLL is a client for the NSRUN.DLL server, which can be called from an
application program. The sequence of calls in this case may be represented by
this diagram:
[End-user application program] -> [NSWRAP.DLL]
-> [NSRUN.DLL]
This feature avoids somewhat complex
and cumbersome OLE-programming, which is otherwise required to build a client
for the NSRUN.DLL.
The nswrap.dll encapsulates 4
functions:
OpenNetwork – This creates a
neural network object and reads the neural network file. It gives you back the number
of inputs the neural network expects and the number of outputs with which it will
respond. Normally, you will already know the number of inputs and outputs. Also,
this function returns the level of the Enhanced Generalization, as it was set up
when you saved the neural network in the Predictor/Classifier. Predictor always return
1 as the number of outputs, Classifier returns the number of output classes as
the number of outputs.
FireNetwork – Once the
neural network is successfully opened with OpenNetwork, use FireNetwork to pass inputs
to the neural network and receive back outputs, both in double precision floating point
arrays which you designate in your program. You will also need to specify the
Enhanced Generalization level at which you want to fire the neural network.
CloseNetwork – Execute this
when you no longer need to execute the neural network. It will release all memory space
and other system resources taken by the neural network. The next time your program
needs to execute the neural network, it will have to do another OpenNetwork.
GetMissingDataSpecifier
– Returns a special constant value to be used as a substitute of the missing
data (if any) in your inputs.
Distribution
Rights
The programs labeled above as distributable may be sold or otherwise distributed outside
of your company or government agency as part of your computer programs or Excel
spreadsheets. You do not have to pay any royalties to provide NSRUN.XLA or NSRUN.DLL with
your programs. The programs labeled NOT distributable may only be sent to employees of
your company or government agency, but not to anyone else including employees of parent or
subsidiary companies or agencies. Programs that may be distributed have the word RUN in
their names. Programs that may not be distributed have the word FIRE in their names.
|



